What is sales data?
Sales data is any information that is machine-readable and of benefit to sales teams. It helps with decision-making, understanding your customers better and improving future performance within your organisation. It is imperative that sales leaders know how to interpret the data they collect and use its insights to improve their sales strategy. Your B2B sales data must be of high quality to gain accurate and timely insights.
By adopting a data-driven approach, your team can sell more predictably and efficiently, which is why sales data analysis is critical for sales success.
In this article, we'll dive into:
- How to find and leverage B2B data for better sales.
- The different types of sales data that can benefit your sales team.
- How to analyse company contact data effectively.
Let's get started 👇 (Or use the menu below to jump to your preferred section)
How do you find sales data for a company? | What are the different types of sales data? | How is data used in sales? |
Examples of sales data | FAQ | Get B2B data for your business
How do you find sales data?
You'll want to invest in a reputable B2B data provider if you're trying to gather business sales data to drive your sales team's performance.
Companies like ZoomInfo, Cognism and Lusha are some of the top choices when choosing a sales data provider.
These lead generation companies can help you:
-
Build accurate prospecting lists
-
Enhance your database with quality GDPR-compliant data
-
Cut time prospecting and focus on closing new business
-
Identify prospects at the right time in their buying journey
An example of leveraging data for increased revenue success can be seen in this case study, where Cognism helped QA generate $81k of opportunities in the first two weeks.
Of course, choosing the right provider can be stressful, but it's all about asking the right questions. Here's a video to help you make the best decision for your business👇.
The five types of sales data
In B2B sales, data is essential to effective decision-making. Sales leaders make decisions in direct response to market changes and customer preferences, and data helps underpin those changes and preferences.
For a successful data-driven sales strategy, you'll want to look at the following five types of data for sales:
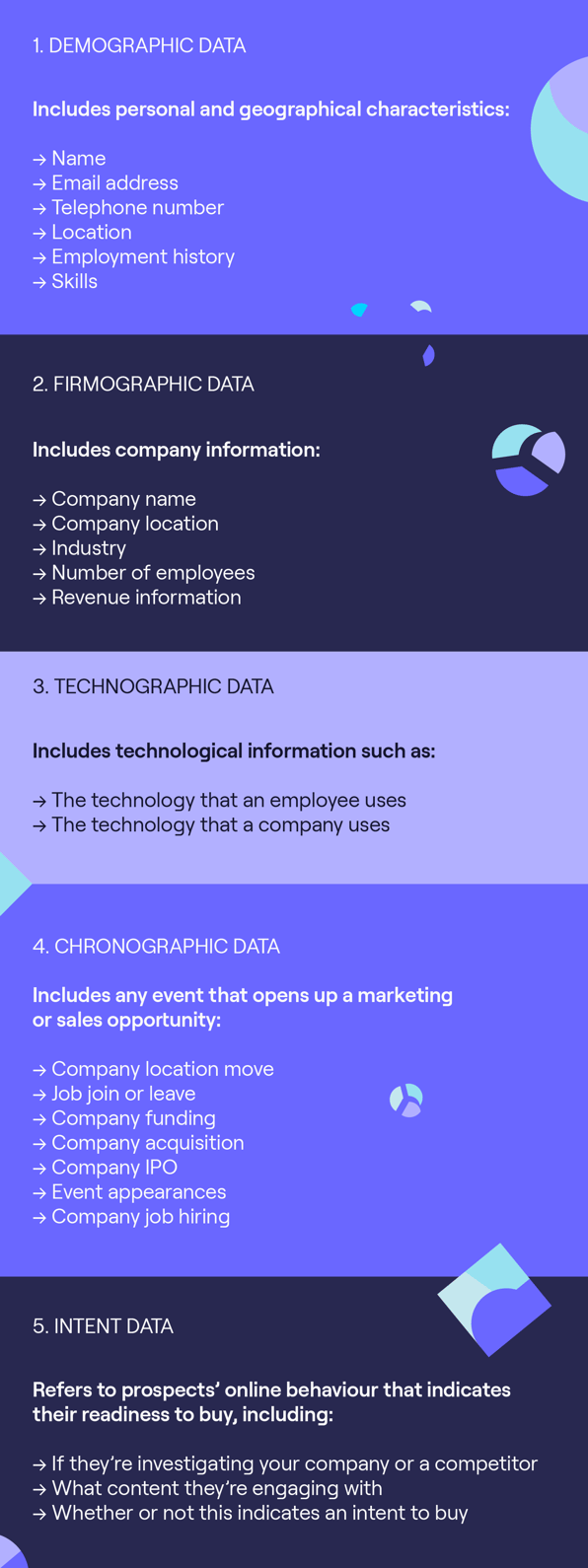
1. Demographic data
Demographic data is essentially geographical sales data. It consists of names, email addresses, telephone numbers, locations, employment histories and skills.
This type of data is the basis for B2B prospecting. It is used to strategically adapt offers to specific target groups for more closed deals.
2. Firmographic data
Essentially the 'demographics of organisations'; this information allows companies to be segmented into defined groups for your SDRs to target. Firmographic data allows you to group companies by unique identifiers.
This type of sales data includes:
- Company name.
- Company location.
- The industry the company operates in.
- Number of employees.
- Revenue information such as ARR.
3. Technographic data
Technographic data refers to the types of tech and software your prospects use daily, whether as individuals or as part of a company.
This type of sales data is extremely useful for business development teams. It allows them to better understand their best-fit prospects' pain points. Then they can easily position their product or service as the solution.
4. Chronographic data
Also known as sales triggers, chronographic data refers to events and changes that occur as time progresses. These changes can lead to an opening to engage with a new prospect or to revisit a prospect that went cold.
Chronographic sales data includes the following: company location moves, a prospect leaving or joining a job, company acquisition, company funding, company IPO, whether the company is hiring or not, and event appearances.
5. Intent data
Sales intent data is behavioural data on a company level. It's based on online customer behaviour that tracks their content consumption and the products they're interested in. Intent data is incredibly valuable in making more efficient and informed sales decisions.
There are two types of intent data:
1. First-party intent data
Data a business collects about their users from their own platforms and website.
2. Third-party intent data
Data collected across several websites, focusing on a specific category. It gives you a more complete view of your prospect's activities across the web.
Using first-party and third-party intent data together is best to avoid overlooking ideal prospects.
How is sales data used?
If your team isn't data-driven, you simply won't keep up with the competition or see results.
Your team can use sales data to:
1. Identify new opportunities
Your SDRs need a quality sales dataset to identify good-fit customers for prospecting. The better the fit, the more likely they will remain loyal and recommend your business to others.
This database must include, as a minimum:
- The names of individuals.
- The names of their companies.
- Job titles.
- Email addresses.
- Direct dial phone numbers.
What's more, sales and marketing data can help sales teams identify which prospects are ready for an upsell or a cross-sell pitch and which are ready to nurture.
This data comes from:
- Reviewing prospects' purchase history and budget - gives you information on your prospects' current solution and their capacity to make a purchase.
- Analysing customer behaviour and building a persona - study the patterns that emerge among your top-performing customers, then use those insights to develop a persona for your ideal sales-ready customer.
- Customer activity data such as automated email campaigns - monitor opens, clicks, and your clickthrough rate.
2. Avoid pursuing bad-fit customers
Selling to bad-fit customers has a significant impact on B2B sales. You'll see higher churn, increased support costs, lowered employee morale, drag on growth and off-target feedback influencing product decisions.
Digital sales data helps you avoid this by allowing you to analyse the following:
- Customer's technical fit - do they need additional tech to get value from your product?
- Functional fit - what do they require from you in order to be successful? Can you provide this?
- Resource fit - do they have the necessary resources to invest in your product?
- Competence fit - do they have the correct expertise to use your product?
- Cultural fit - do their company goals align with yours?
3. Enable effective prospecting
In order to reach and engage with your ideal customers through cold calling, outbound email and social selling, your reps need sales data.
Your SDRs will need the first and last names of prospects, their job titles, company names, business telephone numbers, business email addresses, and website and social media profiles.
Without this information, the process of B2B lead generation is almost impossible.
4. Optimise the sales process
Every sales leader wants to improve the way their team works. To do this, you need to gain insights. It's vital that your B2B sales team tracks and measures data, preferably on a weekly basis; the goal is to fine-tune your process and win long-term customers.
Consistent data tracking can help you pinpoint the bottlenecks in your pipeline. For instance, if a rep's meeting booked rate falls from one week to the next, you can immediately implement a sales training program to get them back up to speed.
Sales data is invaluable for optimising lead generation strategies and processes, such as shortening the sales cycle, aligning sales and marketing goals and monitoring team KPIs.
5. Provide sales forecasts
Sales forecasting empowers you to identify potential issues or risks and implement appropriate corrective actions to mitigate them.
High-quality data will make your forecasting stronger. The sales data you'll want to use here is:
- Income-age.
- Geographical distribution.
- Industry news and press releases.
- Macro-economic factors and sector indexes.
6. Track performance against key objectives
Sales metrics are data points that represent the performance of your team, your organisation, or individual employees. And, when measured against your broader company goals, you can introduce new processes to boost performance.
Some sales metrics you should be tracking include lead velocity, lead cost per conversion, call outcome, SQO pipeline, and sales velocity.
7. Support decision-making
Sales datasets must be consistent and continually updated to support decision-making. Up-to-date data predicts future trends, drives the creation of new business opportunities, optimises operational efforts and ultimately leads to the generation of new business revenue.
Most importantly, implementing a data-driven sales approach should develop, influence, and empower your sales team.
Examples of sales data
Most companies will have a sales database that's frequently refreshed and integrated with a CRM.
For sales data examples and to see the process explained, watch this informative video 👇
FAQ
How do you analyse sales data?
Data should be analysed and enhanced constantly. For effective sales data analysis, follow these two steps:
- Identify key sales metrics - Establish what metrics are important for your team to achieve when closing deals. For example, what are the average deal size and win rate?
- Use a CRM tool like Salesforce to track leads as they enter your pipeline - Review your SalesForce data regularly to monitor your growth rate and immediately pick up any problem areas.
Where is sales data collected from?
A data-driven sales team is capable of producing astonishing results for your company. But they are only as good as the data they use. Where does quality sales data come from?
-
Public sources
Public sources refer to any data freely available and in the public domain.
They include social media profiles, websites and online articles such as blogs or press releases. Another public source is consented-in data; that is, any data that prospects or customers freely supply (e.g., from online form fills or survey results).
-
Private sources
Private B2B sales data sources are secured from public view and must be accessed via a subscription or a form of payment/permission.
They include DaaS (data as a service) providers, paywalled websites and financial/market intelligence platforms.
Get quality data for your team
Improve your lead quality and reach your ideal customers faster with quality GDPR-compliant B2B data.
Cognism offers a sales data service that gives access to direct dial numbers and verified email addresses, updated in real-time.
Book your demo today 👇